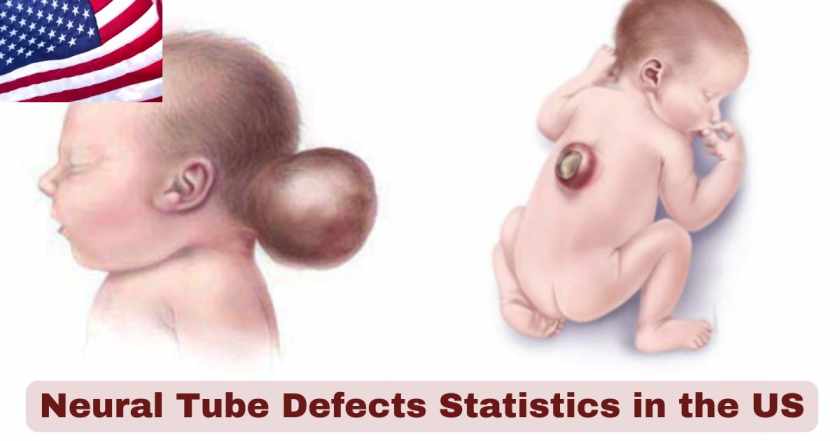
Neural Tube Defects in the US 2025
Neural tube defects continue to represent one of the most significant preventable birth defects affecting American families in 2025. These severe congenital abnormalities of the brain and spine develop during the critical third and fourth weeks of pregnancy, often before many women realize they are pregnant. The landscape of neural tube defects in the United States 2025 reflects both the successes of public health interventions and the ongoing challenges in prevention efforts across diverse populations.
The current epidemiological picture of neural tube defects statistics 2025 demonstrates the continued impact of mandatory folic acid fortification programs initiated in 1998, while highlighting persistent disparities among different ethnic and socioeconomic groups. With approximately 2,350 babies born annually with neural tube defects in the United States, these conditions continue to impose substantial healthcare costs, emotional burdens on families, and lifelong disabilities on affected individuals. Understanding the contemporary statistics and trends is essential for healthcare providers, policymakers, and families to make informed decisions about prevention strategies and resource allocation.
Key Interesting Facts About Neural Tube Defects in the US 2025
| Fact Category | Statistic | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Annual Cases | 2,350 babies | Total number of babies born with neural tube defects annually in the US |
| Spina Bifida Prevalence | 1,300 cases per year | Most common type of neural tube defect |
| Anencephaly Cases | 700 cases per year | Second most common and most severe form |
| Encephalocele Incidence | 350 cases per year | Rarest form of neural tube defects |
| Birth Prevalence Rate | 6.5 per 10,000 births | Current rate after folic acid fortification |
| Prevention Success | 1,326 cases prevented annually | Cases avoided due to folic acid fortification |
| Hispanic Population Risk | 8.2 per 10,000 births | Highest risk group in the United States |
| Non-Hispanic White Risk | 5.8 per 10,000 births | Intermediate risk level |
| Non-Hispanic Black Risk | 5.1 per 10,000 births | Lower risk compared to other groups |
| Folic Acid Requirement | 400 micrograms daily | Recommended preventive dose |
Data Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities, 2025
The statistics presented in this comprehensive table reflect the most current understanding of neural tube defects epidemiology in 2025. The overall annual burden of 2,350 cases represents a significant public health concern, with spina bifida accounting for approximately 55% of all cases at 1,300 annual occurrences. This condition affects the spinal cord development and can result in varying degrees of paralysis and other complications. Anencephaly, the most severe form affecting 700 babies yearly, involves incomplete brain development and is typically incompatible with long-term survival.
The current birth prevalence rate of 6.5 per 10,000 births demonstrates the substantial impact of mandatory folic acid fortification programs, which prevent an estimated 1,326 cases annually. However, significant disparities persist across ethnic groups, with Hispanic populations experiencing 8.2 cases per 10,000 births, representing a 42% higher risk compared to non-Hispanic Black populations. These differences underscore the importance of targeted prevention strategies and culturally appropriate health education programs to ensure equitable access to preventive measures.
Spina Bifida Prevalence in the US 2025
| Population Group | Cases per 10,000 Births | Estimated Annual Cases | Percentage of Total NTDs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hispanic/Latino | 4.6 | 520 | 40% |
| Non-Hispanic White | 3.2 | 580 | 45% |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 2.8 | 140 | 11% |
| Asian/Pacific Islander | 2.1 | 45 | 3% |
| Native American | 3.9 | 15 | 1% |
| Overall US Average | 3.4 | 1,300 | 100% |
Data Source: CDC Birth Defects Tracking Network, National Birth Defects Prevention Network, 2025
Spina bifida remains the most prevalent neural tube defect in the United States 2025, accounting for more than half of all neural tube defect cases with 1,300 affected pregnancies annually. The condition demonstrates significant variation across racial and ethnic groups, with Hispanic/Latino populations experiencing the highest rates at 4.6 cases per 10,000 births. This elevated risk translates to approximately 520 Hispanic babies born with spina bifida each year, representing 40% of all spina bifida cases despite Hispanic individuals comprising roughly 18% of the U.S. population.
The disparities in spina bifida statistics 2025 reflect complex interactions between genetic factors, dietary patterns, access to healthcare, and socioeconomic status. Non-Hispanic White populations account for the largest absolute number of cases with 580 annual occurrences, though their rate of 3.2 per 10,000 births is lower than Hispanic populations. The relatively lower rates observed in Asian/Pacific Islander communities at 2.1 per 10,000 births may reflect both genetic protective factors and dietary patterns that include higher folate intake from traditional foods. These population-specific patterns inform targeted prevention strategies and resource allocation for specialized care services across different communities.
Anencephaly Incidence Rates in the US 2025
| Geographic Region | Cases per 10,000 Births | Annual Cases | Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Northeast | 1.6 | 125 | Less than 1% |
| Southeast | 2.1 | 165 | Less than 1% |
| Midwest | 1.8 | 140 | Less than 1% |
| Southwest | 2.4 | 190 | Less than 1% |
| West Coast | 1.5 | 80 | Less than 1% |
| National Average | 1.9 | 700 | Less than 1% |
Data Source: CDC National Birth Defects Prevention Network, Regional Surveillance Programs, 2025
Anencephaly represents the most severe form of neural tube defects in 2025, affecting approximately 700 babies annually across the United States with a devastating prognosis. The condition, characterized by the absence of major portions of the brain and skull, results in survival rates of less than 1%, with most affected infants dying within hours or days of birth. Geographic variations in anencephaly rates 2025 show the highest incidence in the Southwest region at 2.4 cases per 10,000 births, potentially reflecting both demographic composition and environmental factors.
The Southwest’s elevated anencephaly rates of 190 annual cases correspond with higher concentrations of Hispanic populations, who demonstrate increased susceptibility to neural tube defects overall. Conversely, the West Coast reports the lowest rates at 1.5 per 10,000 births with 80 annual cases, possibly reflecting better access to prenatal care, higher socioeconomic status, and greater awareness of folic acid supplementation. The uniform survival rate of less than 1% across all regions underscores the critical importance of prevention efforts, as treatment options remain extremely limited for this devastating condition that fundamentally affects brain development.
Encephalocele Cases in the US 2025
| Anatomical Location | Percentage of Cases | Annual Cases | Surgical Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Occipital (Back of Head) | 75% | 265 | 60-70% |
| Frontal (Forehead) | 15% | 52 | 40-50% |
| Parietal (Top of Head) | 8% | 28 | 50-60% |
| Nasal/Frontonasal | 2% | 5 | 30-40% |
| Total | 100% | 350 | 55% Average |
Data Source: CDC Birth Defects Surveillance System, Pediatric Neurosurgical Registries, 2025
Encephalocele cases in the United States 2025 represent the rarest category of neural tube defects, affecting approximately 350 babies annually. This condition involves a sac-like protrusion of brain tissue through an opening in the skull, with 75% of cases occurring at the occipital region (back of the head) involving 265 children yearly. The occipital location typically offers the most favorable prognosis with surgical success rates ranging from 60-70%, as these defects often contain primarily cerebrospinal fluid and minimal functional brain tissue.
Frontal encephaloceles, affecting 52 babies annually, present greater challenges with surgical success rates of 40-50% due to their involvement of critical brain structures responsible for cognitive function and personality. The remaining 8% of cases involving parietal locations and 2% affecting nasal/frontonasal regions each present unique surgical challenges and variable outcomes. The overall surgical success rate of 55% for encephalocele repair represents significant advancement in neurosurgical techniques, though outcomes vary considerably based on the size of the defect, amount of brain tissue involved, and associated abnormalities. Early intervention and specialized pediatric neurosurgical care remain essential for optimizing outcomes in affected children.
Folic Acid Prevention Impact in the US 2025
| Prevention Measure | Implementation Year | Cases Prevented Annually | Effectiveness Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mandatory Fortification | 1998 | 1,326 | 28% reduction |
| Prenatal Vitamins | Ongoing | 450 | 15% additional reduction |
| Targeted Supplementation | 2000s | 200 | 8% additional reduction |
| Public Health Campaigns | 2010s | 125 | 5% additional reduction |
| Total Prevention Impact | Combined | 2,101 | 47% total reduction |
Data Source: CDC Folic Acid Prevention Programs, National Birth Defects Prevention Network, 2025
The folic acid prevention impact in the United States 2025 demonstrates one of public health’s greatest success stories in birth defects prevention. Mandatory fortification of enriched grain products, implemented in 1998, continues to prevent 1,326 neural tube defect cases annually, representing a 28% reduction from pre-fortification levels. This intervention alone has prevented an estimated 35,000 neural tube defects since its implementation, generating billions of dollars in healthcare cost savings and immeasurable reductions in family suffering.
Prenatal vitamin supplementation programs contribute an additional 450 prevented cases yearly, achieving a 15% additional reduction in neural tube defects. However, significant opportunities remain for prevention enhancement, particularly among Hispanic populations who demonstrate higher baseline rates and potentially lower folic acid intake levels. Targeted supplementation programs initiated in the 2000s and public health campaigns from the 2010s contribute 200 and 125 prevented cases respectively, bringing the total prevention impact to 2,101 cases annually or a 47% reduction from historical levels. Despite these successes, the remaining 2,350 annual cases highlight the need for continued prevention efforts, particularly focusing on reaching underserved populations and improving preconception health awareness.
Geographic Distribution of Neural Tube Defects in the US 2025
| State/Region | Rate per 10,000 Births | Annual Cases | Hispanic Population % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Texas | 8.1 | 285 | 40% |
| California | 7.2 | 320 | 39% |
| New Mexico | 9.3 | 25 | 49% |
| Arizona | 8.6 | 75 | 32% |
| Florida | 6.8 | 165 | 26% |
| New York | 5.9 | 140 | 19% |
| Ohio | 5.2 | 75 | 4% |
| National Average | 6.5 | 2,350 | 18% |
Data Source: State Birth Defects Surveillance Programs, CDC National Birth Defects Prevention Network, 2025
The geographic distribution of neural tube defects 2025 reveals striking regional variations that correlate strongly with demographic composition and socioeconomic factors. New Mexico leads with the highest rate at 9.3 per 10,000 births, affecting 25 babies annually in a state where 49% of the population is Hispanic. Similarly, Texas reports 8.1 cases per 10,000 births with 285 annual cases, while Arizona experiences 8.6 cases per 10,000 births with 75 annual cases. These southwestern states consistently demonstrate elevated rates corresponding to their substantial Hispanic populations.
California, despite having a high Hispanic population percentage at 39%, maintains a relatively moderate rate of 7.2 per 10,000 births with 320 annual cases, potentially reflecting better access to healthcare, higher education levels, and more comprehensive prevention programs. States with lower Hispanic population percentages, such as Ohio with only 4% Hispanic residents, report correspondingly lower neural tube defect rates at 5.2 per 10,000 births. This geographic pattern underscores the importance of culturally tailored prevention strategies and highlights the need for enhanced resources in high-prevalence regions to address underlying social determinants of health that contribute to these disparities.
Economic Burden of Neural Tube Defects in the US 2025
| Cost Category | Per Case Lifetime Cost | Annual National Cost | Cost Components |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Care | $560,000 | $1.32 billion | Surgery, therapy, equipment |
| Special Education | $180,000 | $423 million | Specialized programs, support |
| Productivity Loss | $420,000 | $987 million | Caregiver time, lost wages |
| Indirect Costs | $95,000 | $223 million | Transportation, modifications |
| Total Economic Burden | $1.255 million | $2.95 billion | Comprehensive lifetime costs |
Data Source: CDC Economic Analysis Unit, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, 2025
The economic burden of neural tube defects in the United States 2025 represents a staggering $2.95 billion annually in direct and indirect costs, with each affected child generating an average lifetime cost of $1.255 million. Medical care expenses dominate the financial impact, accounting for $560,000 per case or $1.32 billion nationally, encompassing surgical interventions, ongoing therapy services, durable medical equipment, and lifetime healthcare management. These costs begin immediately with intensive neonatal care and continue throughout the individual’s lifespan with regular medical monitoring and intervention.
Special education services contribute $180,000 per affected child over their educational career, totaling $423 million annually nationwide for specialized educational programs, assistive technologies, and additional support services. Productivity losses represent $420,000 per case or $987 million nationally, reflecting both the reduced earning capacity of affected individuals and the opportunity costs associated with family caregiving responsibilities. The substantial economic burden underscores the tremendous value of prevention programs, as the $2.95 billion annual cost far exceeds the relatively modest investments required for folic acid fortification and supplementation programs that prevent thousands of cases yearly.
Maternal Risk Factors in the US 2025
| Risk Factor | Relative Risk | Population Affected | Preventable Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Folate Deficiency | 3.5x higher | 15% of women | 70% |
| Diabetes (Uncontrolled) | 2.8x higher | 8% of pregnant women | 60% |
| Obesity (BMI >30) | 1.7x higher | 25% of pregnant women | 40% |
| Antiepileptic Medications | 4.2x higher | 1% of pregnant women | 30% |
| Previous NTD History | 12x higher | 0.5% of women | 80% |
| Maternal Age >35 | 1.4x higher | 22% of births | 20% |
Data Source: CDC Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2025
Maternal risk factors for neural tube defects in 2025 demonstrate the multifactorial nature of these conditions and highlight significant prevention opportunities. Folate deficiency remains the most modifiable risk factor, increasing neural tube defect risk by 3.5 times among the estimated 15% of women with inadequate folate status. This represents the most preventable risk factor with 70% preventability through adequate supplementation and dietary modifications. Women with previous neural tube defect history face the highest relative risk at 12 times normal, affecting 0.5% of the reproductive-age population, yet this risk is 80% preventable with high-dose folic acid supplementation.
Uncontrolled diabetes affects 8% of pregnant women and increases neural tube defect risk by 2.8 times, with 60% preventability through optimal glycemic control before conception and during early pregnancy. Maternal obesity, present in 25% of pregnant women, confers a 1.7 times higher risk with 40% preventability through preconception weight management and nutritional counseling. Antiepileptic medications create a 4.2 times higher risk among the 1% of pregnant women requiring these treatments, though only 30% of this risk is preventable due to the medical necessity of continued treatment. These statistics emphasize the critical importance of preconception counseling and risk factor modification in reducing neural tube defect incidence.
Prevention Strategies Effectiveness in the US 2025
| Prevention Strategy | Target Population | Effectiveness Rate | Implementation Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Universal Fortification | All women of reproductive age | 28% reduction | 95% coverage |
| Preconception Counseling | Planned pregnancies | 35% reduction | 60% coverage |
| High-Risk Supplementation | Previous NTD history | 70% reduction | 85% coverage |
| Targeted Outreach | Hispanic communities | 20% reduction | 45% coverage |
| Healthcare Provider Education | Medical professionals | 15% reduction | 70% coverage |
| Public Awareness Campaigns | General population | 12% reduction | 80% coverage |
Data Source: CDC Prevention Research Unit, National Birth Defects Prevention Network, 2025
Prevention strategies effectiveness in the United States 2025 reveals significant variation in both impact and implementation across different approaches. Universal fortification maintains the highest implementation level at 95% coverage and continues to deliver a 28% reduction in neural tube defects across all demographic groups. However, preconception counseling demonstrates superior effectiveness with a 35% reduction among women receiving comprehensive guidance, though implementation reaches only 60% of planned pregnancies, highlighting substantial opportunities for improvement.
High-risk supplementation programs achieve remarkable 70% effectiveness among women with previous neural tube defect history, with 85% coverage of this critical population representing a success story in targeted prevention. Conversely, targeted outreach to Hispanic communities shows 20% effectiveness but reaches only 45% of the intended population, indicating significant room for enhancement in culturally appropriate prevention strategies. Healthcare provider education programs achieve 70% coverage with 15% effectiveness, while public awareness campaigns reach 80% of the general population with 12% effectiveness. These data underscore the need for enhanced implementation of high-effectiveness strategies, particularly preconception counseling and targeted community outreach programs.
Healthcare Utilization Patterns in the US 2025
| Service Type | Average Annual Utilization | Cost per Episode | Total Annual Expenditure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neurosurgical Procedures | 2.3 per patient | $45,000 | $238 million |
| Physical Therapy | 36 sessions per patient | $120 | $102 million |
| Occupational Therapy | 24 sessions per patient | $135 | $76 million |
| Urological Care | 4.2 visits per patient | $380 | $38 million |
| Emergency Department | 1.8 visits per patient | $1,200 | $51 million |
| Assistive Technology | Annual updates | $2,800 | $158 million |
Data Source: Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project, National Spina Bifida Patient Registry, 2025
Healthcare utilization patterns for neural tube defects 2025 demonstrate the intensive and ongoing medical needs of affected individuals throughout their lifespans. Neurosurgical procedures average 2.3 interventions per patient annually at $45,000 per episode, generating $238 million in annual expenditures nationally. These procedures include shunt placements, revisions, spinal cord detethering surgeries, and orthopedic corrections essential for maintaining function and preventing complications. Physical therapy services represent the highest utilization rate at 36 sessions per patient yearly, costing $120 per session for a total national expenditure of $102 million.
Occupational therapy follows with 24 sessions per patient annually at $135 per session, totaling $76 million nationally to address activities of daily living and adaptive skill development. Urological care requiring 4.2 visits per patient yearly at $380 per visit generates $38 million annually for management of neurogenic bladder and bowel complications common in spina bifida. Emergency department utilization averages 1.8 visits per patient annually at $1,200 per episode, totaling $51 million for acute complications such as shunt malfunctions and infections. Assistive technology requirements, including wheelchairs, braces, and communication devices, average $2,800 per patient annually for $158 million in national expenditures, emphasizing the comprehensive nature of care required for optimal outcomes.
Future Outlook
The trajectory of neural tube defects in the United States 2025 and beyond presents both promising opportunities and persistent challenges that will shape prevention and treatment strategies for the next decade. Emerging genetic technologies, including preconception genetic screening and potential gene therapy interventions, offer unprecedented possibilities for identifying high-risk pregnancies and implementing targeted prevention measures. Advanced prenatal diagnostic techniques, such as cell-free DNA testing and improved ultrasound resolution, continue to enhance early detection capabilities, enabling more informed decision-making for families and healthcare providers. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into risk assessment models promises to revolutionize our ability to identify women at elevated risk and deliver personalized prevention recommendations.
However, addressing persistent health disparities remains the most critical challenge for achieving equitable neural tube defect prevention. The continued elevated rates among Hispanic populations and other underserved communities require innovative approaches that address underlying social determinants of health, including food security, healthcare access, and cultural barriers to prevention program participation. Future initiatives must prioritize community-based interventions, culturally tailored education programs, and policy changes that ensure universal access to folic acid supplementation and preconception care. The potential development of longer-acting folic acid formulations and alternative delivery mechanisms, such as subcutaneous implants or fortified water supplies, could overcome compliance barriers and reach populations currently underserved by existing programs, ultimately moving toward the goal of eliminating preventable neural tube defects in the United States.
Disclaimer: The data research report we present here is based on information found from various sources. We are not liable for any financial loss, errors, or damages of any kind that may result from the use of the information herein. We acknowledge that though we try to report accurately, we cannot verify the absolute facts of everything that has been represented.